Back to blog
AI Security Training Platforms: Which Features Matter?

Written by
Brightside Team
Published on
Feb 9, 2026
Every security leader knows the statistic by now. Human error causes somewhere between 68% and 95% of all security breaches. You've probably invested in security awareness training to fix this problem. Maybe you're running phishing simulations every quarter. Your completion rates look good on paper.
But here's what the data also shows: 64% of IT and security professionals clicked phishing links in the past year, even though 80% of them believed they were resistant to these attacks. Something isn't working.
The problem isn't that training fails entirely. Organizations that implement security awareness programs do report 65% to 72% reductions in employee-driven incidents. The problem is that most programs measure the wrong things and train for the wrong threats.
If your platform still focuses mainly on email phishing templates and tracks completion rates, you're solving 2018's problem. Attackers now use deepfake audio to impersonate your CFO, AI-generated emails that mirror your writing style, and multi-step social engineering across email, text, and phone calls. Deepfake-enabled scams increased 3,000% from 2022 to 2023. Yet only 20% of training programs address voice phishing or deepfakes.
This article will help you evaluate AI security awareness platforms based on what actually reduces risk, not what looks good in a quarterly report.
What "AI Security Awareness" Should Mean in 2026
First, let's clear up some confusion. The security awareness training market has split into two categories that sound similar but work very differently.
Security Awareness Training (SAT) focuses on education. You deliver training modules, run scheduled phishing tests, and measure who completed what. The goal is knowledge transfer. Did employees learn about phishing? Can they pass a quiz?
Human Risk Management (HRM) focuses on behavior measurement and risk reduction. You continuously monitor how employees actually behave under pressure, identify high-risk individuals before incidents occur, and deliver interventions triggered by real actions, not calendars. The goal is measurable risk reduction. Did risky behaviors decrease?
Think of it this way. SAT asks, "Did you attend the fire safety class?" HRM asks, "Do you still prop the emergency exit open with a brick?"
The distinction matters because these platforms use fundamentally different architectures. Traditional SAT platforms retrofitted AI features onto content libraries built years ago. They select from thousands of pre-made templates and personalize subject lines using basic variables. HRM platforms built their architecture around behavioral data collection first, with training as the output rather than the product.
Most vendors now slap "AI-powered" on their marketing pages. Your job is to figure out which ones actually use AI to change outcomes.
The AI Features That Actually Change Outcomes
Not all AI features deliver equal value. Some represent genuine innovation. Others are marketing labels on unchanged systems. Here's how to tell the difference.
OSINT-Powered Personalization
Open Source Intelligence (OSINT) means scanning publicly available information to understand someone's digital footprint. For security training, this means your platform scans what attackers would scan: social media profiles, data breach databases, professional networking sites, and public records.
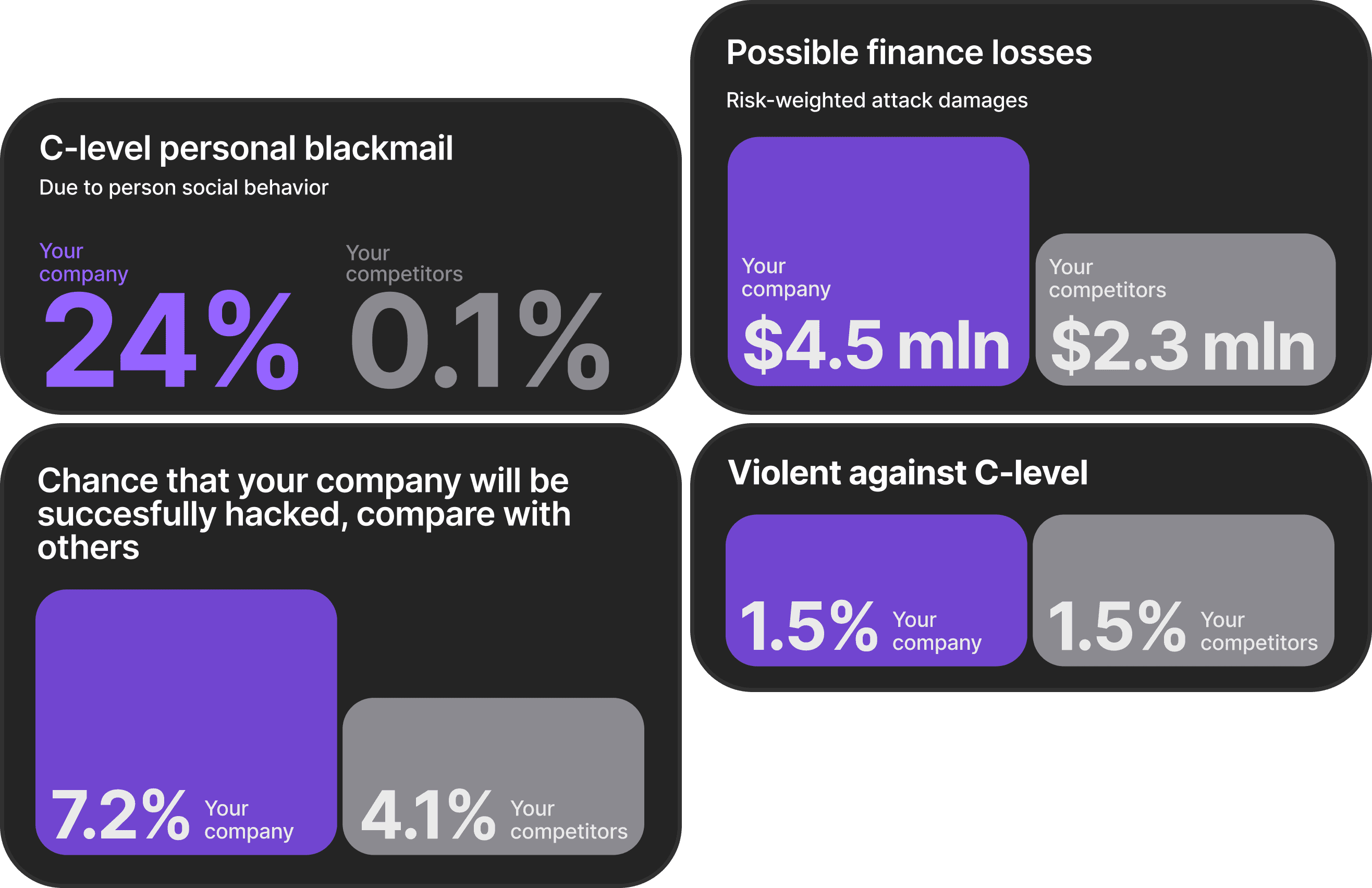
Why does this matter? Personalized phishing attacks succeed 50% to 80% more often than generic ones. If your training only uses generic templates, you're not preparing employees for the attacks they'll actually face.
Platforms using comprehensive OSINT scan six categories: personal information (email addresses, phone numbers, home addresses), data leaks (compromised passwords found in breaches), online services (LinkedIn, entertainment platforms, dating sites), personal interests (hobbies, forum participation), social connections (who they interact with online), and locations (where they live and travel).
This enables simulations that reference real coworkers by name, mention actual projects employees work on, and reference recent business travel. When an employee sees their home address and family member names appearing in a simulated attack, the threat stops being abstract.
Some vendors call this invasive. The better platforms handle this through proper architectures. Employees see their own complete digital footprint and get tools to reduce exposure. Administrators see only aggregate risk scores without personal details. This respects privacy while reducing organizational attack surface.
Generative Attack Simulations
Template-based platforms select from libraries of pre-built phishing emails. They might have 1,000 or even 5,000 templates. This sounds impressive until you realize employees start recognizing the patterns.
One practitioner put it bluntly when reviewing a major platform: rates "under 2% mean your lures are probably too easy" and "users have mostly learned how to spot the specific variants you are using".
Generative AI platforms work differently. They create novel attacks rather than selecting from templates. These systems use large language models trained on actual phishing corpora to replicate attacker writing styles. Some use Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs), where one AI generates convincing attacks while another evaluates how realistic they appear, forcing continuous improvement.
Every simulation can be unique, matching your industry's communication patterns, your company's writing style, and current events relevant to your business.
Organizations implementing continuous adaptive simulations achieved 50% compromise rate reductions within six months, compared to 40% reductions over 90 days for traditional template approaches.
Multi-Channel Coverage
Email phishing represents only one attack vector. Modern threat actors increasingly combine multiple channels in coordinated attacks.
The typical sequence looks like this: a realistic phishing email establishes credibility, an SMS message creates urgency ("Confirm this transaction now"), and a phone call using AI-cloned voice closes the attack ("This is your CFO. I need that wire transfer approved immediately").
With only a few seconds of publicly available audio, AI can now replicate executive voices across 40+ languages. Phone-based verification has become "effectively meaningless".
Yet 80% of training programs still focus exclusively on email.
Comprehensive platforms now simulate email phishing with OSINT personalization, SMS attacks (smishing) optimized for mobile devices, voice phishing (vishing) using AI-generated audio, deepfake video targeting executives, QR code attacks (quishing) that bypass email filters, and messaging app threats through Teams, Slack, or WhatsApp.
If your program doesn't address these channels, you're leaving attack surfaces undefended.
Behavioral Risk Scoring
This is where HRM platforms separate from traditional SAT tools. Instead of measuring whether someone completed training, these systems measure actual risky behaviors across your environment.
Advanced platforms track 50 to 100+ distinct behaviors including permissions misuse (requesting access beyond role requirements), MFA fatigue (approving authentication requests without verification), data handling practices (storing sensitive information in unauthorized locations), and approval workflow anomalies (bypassing normal verification procedures).
The system assigns risk scores predicting incident likelihood based on behavioral patterns, not training completion. High-risk users face additional authentication requirements, limited lateral movement permissions, and just-in-time training before accessing sensitive resources.
One platform reports that 60% to 80% of their training interventions now trigger based on live behavioral telemetry rather than calendar schedules. That represents a fundamental shift from "everyone gets quarterly training" to "this person just did something risky and needs intervention right now."
Real-Time Integration
The most sophisticated deployments connect security awareness platforms with Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) systems. When your SIEM detects risky behavior (unusual login locations, sensitive data access at odd hours, suspicious file downloads), the integrated training platform automatically delivers targeted micro-training within seconds.
This creates automated loops: detect risky behavior, deliver immediate training, enforce policy if behavior repeats. Organizations implementing these loops report 20% to 40% reductions in repeated risky actions over 90 days.
This requires platforms supporting 30+ native integrations with your existing security stack. Legacy SAT tools typically support only 1 to 5 integrations.
Metrics That Prove Risk Reduction
Most organizations measure security awareness training success using completion rates and quiz scores. These metrics tell you almost nothing about actual risk reduction.
Think about it. An employee can score 100% on a phishing quiz but still click a sophisticated spear-phishing email under deadline pressure. The quiz measured knowledge. The click revealed behavior.
Here are the metrics that actually matter.
Credential Compromise Rate: What percentage of employees not only clicked a phishing simulation but also entered their username and password? Industry benchmarks show 6.5% of people who click phishing simulations submit credentials, with 60% of clickers eventually compromising credentials. Target rates should fall below 0.5%.
Payload Download Rate: What percentage downloaded a malicious attachment or ran executable code? Target rates should fall below 0.1%.
Time-to-Report: How quickly do employees report suspicious messages after receiving them? Faster reporting enables faster incident response. Platforms that enable one-click reporting from email clients achieve 3x higher reporting rates than those requiring separate portals.
Resilience Ratio: This measures reports divided by failures. One documented case study showed a 526% increase in reporting rate combined with a 79% decrease in failure rate, producing a 2,533% resilience ratio improvement. This metric captures both avoidance behavior and active threat hunting.
Real-Threat Reporting Accuracy: Are employees reporting actual suspicious emails they receive, not just your simulations? Some organizations see thousands of employee reports after implementing reporting-focused training, with 5% to 15% representing genuine threats that security teams can investigate.
These metrics require platforms built to track behavioral outcomes, not just content engagement.
Platform Comparison: 5 Enterprise Options
Let's look at five platforms representing different approaches to AI-powered security awareness training.
KnowBe4: The Enterprise Standard
KnowBe4 dominates the market through operational simplicity at enterprise scale. The platform offers a library of 1,000+ training modules across 40+ languages, straightforward employee onboarding and assignment tracking, extensive compliance documentation for regulated industries, and proven track records in financial services, healthcare, and government.
The platform achieves a 4.7 out of 5 G2 rating across thousands of reviews, primarily praised for administrative efficiency.
Where it shows limitations: multiple reviewers note that simulations remain "email-centric and template-driven" without comprehensive deepfake, vishing, or multi-channel scenarios. The templates "follow older, recognizable patterns" with "slower adaptation to emerging threats". The platform provides neither "deep behavioral analytics" nor "predictive capability" to forecast where incidents will occur.
Best fit: Large enterprises in regulated industries requiring proven compliance documentation and broad content libraries for global workforces.
Hoxhunt: Engagement Through Gamification
Hoxhunt differentiates through behavioral conditioning psychology. The platform delivers frequent adaptive simulations timed around work hours in local languages, provides immediate contextual micro-training after clicks or reports, and deploys points, badges, and leaderboards to drive participation.
The documented effectiveness is impressive. One case study with International Game Technology showed a 526% reporting rate increase, 79% failure rate decrease, and 2,533% resilience ratio increase.
The platform achieves a 4.8 out of 5 G2 rating.
Where it shows limitations: some reviewers warn about "over-reliance on gamification" where "users treat simulations as a game rather than learning, clicking or reporting carelessly just to improve their score". Others note "repetition in simulation difficulty and variety" with scenarios feeling "predictable or too easy over time".
Best fit: Organizations struggling with training engagement and needing to build reporting culture across their workforce.
Brightside AI: OSINT-Powered Dual Protection
Brightside AI takes the most architecturally distinctive approach by recognizing that employee personal digital footprints create organizational vulnerabilities. The Swiss-based platform combines enterprise security training with individual privacy management.
The platform scans six categories of OSINT data: personal information, data leaks, online services, interests, social connections, and locations. This generates Personal Safety Scores based on exposed data types, relevance to safety goals, and attack surface combinations.
The dual-portal architecture gives employees direct visibility into their exposed data with guided remediation through the Brighty privacy companion. Administrators see aggregate risk scores and vulnerability trends without accessing personal details. The platform includes automated data broker removal, reducing intelligence available to attackers before they craft attacks.
Training delivery happens through chat-based courses with gamification elements, making complex concepts accessible. Simulations cover email phishing, vishing, and deepfake videos, with each leveraging OSINT data for maximum personal relevance.
Where it requires consideration: OSINT-powered training makes threats feel very personal. Organizations need careful messaging around privacy boundaries and how employee data gets used.
Best fit: Organizations wanting OSINT-powered simulation realism combined with proactive digital footprint reduction, creating shared ownership of security outcomes.
OutThink: Human Risk Management Pioneer
OutThink leads the Human Risk Management category by focusing on continuous behavioral measurement rather than scheduled training. The platform measures 80+ behavioral risk factors beyond phishing, delivers real-time coaching through Teams, Outlook, and Gmail integration, and provides predictive Human Risk Intelligence scores.
The operational shift is significant. OutThink reports 60% to 80% of training interventions now trigger based on live telemetry rather than calendar schedules, with 3x higher engagement rates through personalized nudges.
The system tracks risky behaviors including permissions misuse, MFA fatigue, data handling practices, and approval workflow anomalies. This comprehensive behavioral intelligence enables integration with Zero Trust architectures where risk scores influence access decisions dynamically.
Where it requires consideration: implementing HRM requires clearer governance frameworks around what behaviors you measure and how you act on behavioral data. Organizations need policies addressing employee privacy concerns about continuous monitoring.
Best fit: Mature security programs pursuing measurable risk reduction through behavioral intelligence and wanting integration with broader security operations.
Adaptive Security: AI-Native Threat Realism
Adaptive Security positions as the technical sophistication leader, built specifically for organizations facing AI-enabled attacks. The platform received investment from OpenAI as their first cybersecurity portfolio company, signaling credible technical depth.
The core strength lies in simulation realism across multiple attack vectors. Users report the ability to "actually easily make extremely specific content tailored to our company and industry" through the AI Content Creator. The platform simulates deepfake audio calls targeting finance teams, AI-generated emails mimicking internal writing styles, SMS and messaging app attacks, and multi-step social engineering sequences.
Behavioral analytics provide "risk scores from real behaviors, not on whether employees 'completed training'", contextualized by role and industry benchmarks.
Integration depth includes connections with Okta, Rippling, BambooHR, Slack, and Microsoft Teams, ensuring "employee lists and groups stay up to date automatically".
Where it requires consideration: higher realism in simulations can increase internal scrutiny. Organizations need strong change management when implementing deepfake scenarios that can feel unsettlingly personal.
Best fit: Organizations facing sophisticated, AI-driven social engineering threats and needing multi-channel simulation realism.
Start your free risk assessment
Our OSINT engine will reveal what adversaries can discover and leverage for phishing attacks.
What Actually Matters in 2026
The security awareness training market has matured beyond awareness into quantifiable risk management. Human error driving 68% to 95% of breaches represents a measurable, manageable risk factor when you use the right tools and measure the right things.
Three trends will define platform selection over the next 18 months.
Multi-channel coverage becomes mandatory. With deepfake scams increasing 3,000% annually and attackers exploiting voice, SMS, and messaging channels, email-only training creates dangerous blind spots. Platforms unable to demonstrate proficiency across these vectors will struggle as comprehensive coverage becomes standard.
OSINT integration separates leaders from followers. Generic template-based training cannot match the realism and effectiveness of simulations powered by comprehensive digital footprint analysis. The dual benefit of realistic training plus proactive exposure reduction justifies premium pricing.
Behavioral measurement replaces completion metrics. Organizations tracking credential compromise rates, resilience ratios, and time-to-report will outperform those celebrating high completion percentages. Success requires platforms built to measure behavior, not engagement.
The vendors winning enterprise deployments demonstrate genuine AI innovation through comprehensive OSINT scanning, generative attack simulation, and predictive behavioral analytics. They provide tools to identify, predict, and mitigate human risk systematically.
Organizations that select platforms based on content volume or completion rates will underperform those evaluating behavioral intelligence depth, multi-channel coverage breadth, and architectural sophistication. The choice you make now determines whether your workforce remains your weakest link or becomes your strongest defense.