Back to blog
Security Awareness Training 2025: Tools, Trends & ROI

Written by
Brightside Team
Published on
Nov 3, 2025
Your quarterly training program might be leaving your organization wide open to attack. Think about it this way: your employees complete their annual security training in January, click through the final slide, and mark it done. Fast forward to November. Do they remember which email links to avoid? Can they spot a deepfake voice message from a cybercriminal pretending to be your CFO? The answer is probably no.
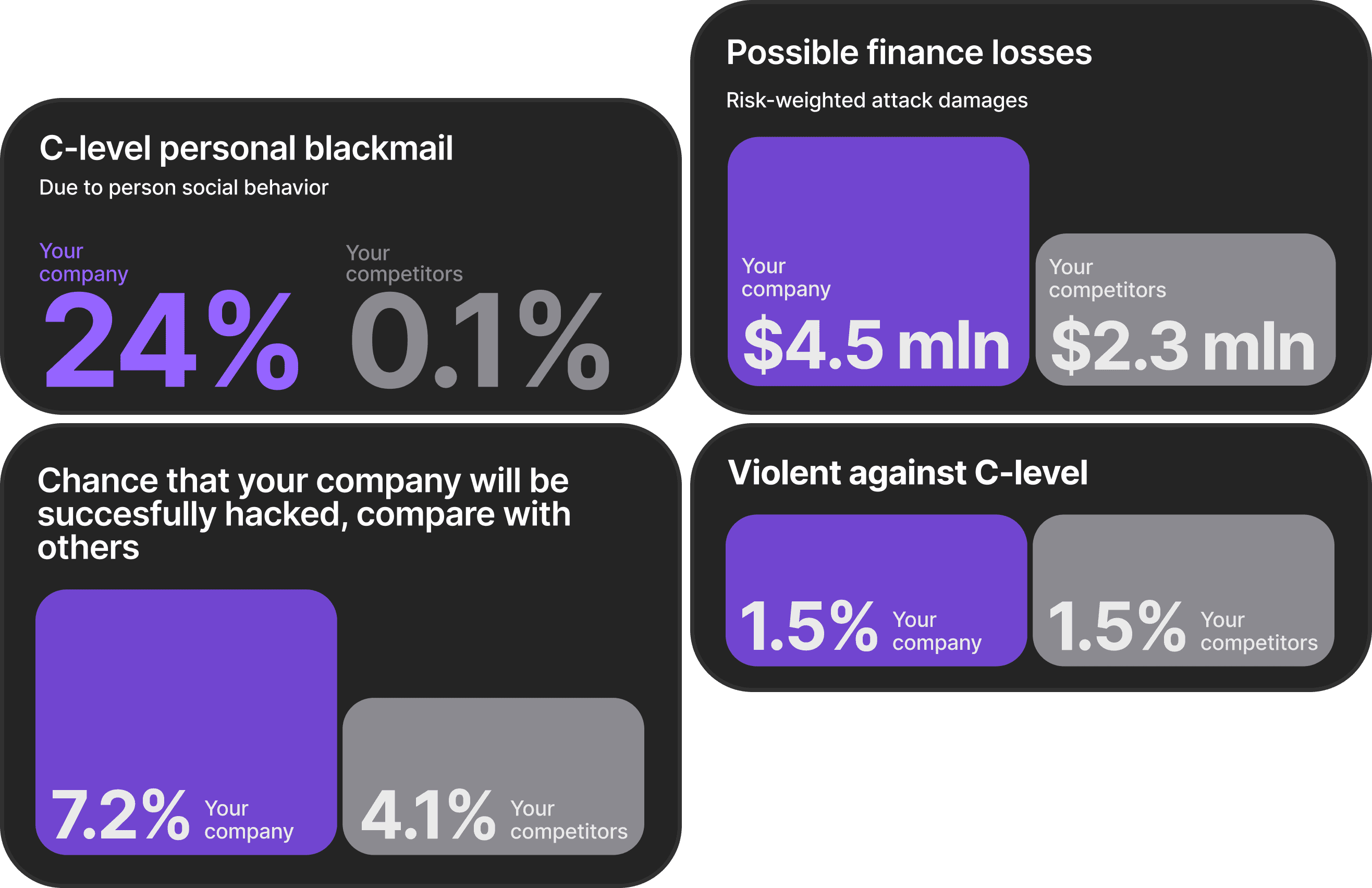
The problem runs deeper than poor memory. Traditional security awareness training achieves just 7% reporting rates when employees encounter suspicious messages. Meanwhile, 68% of data breaches involve human factors, and 82% trace back to human error. Your people aren't the problem. The training is.
This guide breaks down what's changing in security awareness training for 2025. You'll learn why the old quarterly model fails, which new approaches actually work, and how to measure real results instead of just checking compliance boxes. Whether you're a CISO rebuilding your security culture or a CEO evaluating training investments, you'll walk away with practical strategies backed by current data.
Let's start with what security awareness training really means. It's ongoing education that teaches employees to recognize cyber threats and respond correctly. Not a one-time event. Not a yearly video. Ongoing.
Security awareness describes the knowledge your team collectively holds about identifying and handling cyber risks. It's what your finance team does when they get a suspicious wire transfer request. It's whether your engineers question an unexpected IT support call asking for credentials.
Security awareness training for employees takes this further by personalizing education based on individual roles and risk exposure. Your HR team faces different threats than your development team. Effective training recognizes this reality.
The market reflects growing urgency. The global cybersecurity training market hit $4.53 billion in 2023 and will reach $13.70 billion by 2030. Organizations now spend $0.45 to $6.00 per user monthly on training programs. This investment responds to regulations like NIS2 and DORA while pursuing measurable returns through reduced breach costs and improved incident response.
Understanding Traditional Training Limitations
Most organizations follow a predictable pattern. Annual or quarterly training sessions. Standardized content. Everyone gets the same material regardless of whether they work in finance, engineering, or customer service.
The results tell the story. Those quarterly programs achieve just 7% phishing simulation reporting rates. Even more concerning: 70% of organizations running active training programs still observe insecure employee behaviors.
Why does traditional training fail so consistently?
Generic content doesn't connect with how people actually work. Your finance team receives wire transfer requests daily. They face different attack patterns than your engineering staff who manage code repositories and cloud infrastructure. Yet both groups sit through identical training modules covering broad security concepts rather than role-specific threats.
Annual or quarterly delivery creates massive knowledge gaps. Employees receive training, then go 9-11 months without reinforcement. Cybercriminals don't take breaks. They send 3.4 billion phishing attacks daily, many incorporating AI-generated deepfakes and hyper-personalized content targeting specific individuals. Your team needs continuous preparation, not yearly refreshers.
Compliance-focused mindsets compound these problems. Organizations celebrate 99% training completion rates while missing the critical metric: employees take just 21 seconds to click malicious links after opening phishing emails. Completing a course doesn't equal behavior change. Most traditional programs measure the wrong things entirely.
The shift from compliance to impact requires fundamental changes. You can't fix outdated training by making it prettier or adding more slides. You need different approaches built around how people learn and what actually changes behavior.
Emerging Training Trends for 2025
The security training landscape is evolving rapidly. Organizations implementing next-generation approaches see dramatically different results compared to those stuck with legacy programs.
Adaptive and Continuous Models
Remember that 7% reporting rate from traditional quarterly training? Adaptive security awareness training flips those numbers. Organizations implementing adaptive programs achieve 60% reporting rates after one year. That's not a small improvement. It's a fundamental transformation in how employees respond to threats.
What makes adaptive training different?
Continuous micro-learning replaces quarterly events with short, frequent sessions woven into the workweek. Instead of sitting through hour-long compliance videos, employees spend 5-10 minutes learning specific skills they can apply immediately. This approach maintains engagement without disrupting productivity.
Personalized content addresses individual risk profiles. The system analyzes employee roles, digital footprints, and performance in previous simulations, then delivers targeted training addressing specific vulnerabilities. Someone who repeatedly clicks links in simulated phishing emails receives different content than someone who consistently reports suspicious messages.
Regular assessment through phishing simulations creates feedback loops identifying who needs additional support. These aren't gotcha moments meant to embarrass employees. They're data points revealing where your training program needs adjustment.
Organizations implementing adaptive models report 47% reductions in identity-related security incidents and 62% improvements in incident response times. Only 7.5% of organizations currently use adaptive training programs, creating competitive advantages for early adopters.
AI-Powered Threat Simulations
Cybercriminals already weaponized AI. About 82.6% of phishing emails now contain AI-generated content, while 46% of organizations face deepfake attacks targeting executives and finance teams.
Your training needs to match this sophistication.
Advanced simulation platforms deploy realistic scenarios across multiple attack vectors. Email phishing simulations leverage OSINT data to create hyper-personalized spear phishing attempts mirroring actual threat actor tactics. Instead of obvious fake emails from "Nigerian princes," employees encounter messages referencing real projects, actual colleagues, and legitimate business processes.
Voice phishing simulations prepare teams for the growing vishing threat. AI-generated phone calls impersonate IT support requesting credentials or executives approving urgent wire transfers. These scenarios train employees to recognize social engineering in voice communications, not just written messages.
Deepfake simulations address the emerging frontier of AI manipulation. Employees practice identifying AI-manipulated video and audio impersonating executives. When your CFO's face and voice can be faked convincingly, your team needs experience recognizing subtle indicators that something's wrong.
OSINT-driven personalization represents a breakthrough in simulation realism. Platforms scanning employee digital footprints identify publicly exposed data like work emails on LinkedIn, personal information on data broker sites, and social media connections that attackers exploit. Simulations incorporating this real-world data demonstrate actual vulnerabilities rather than hypothetical scenarios. The educational impact is significantly higher when employees see their own exposed information used in simulated attacks.
Gamification and Engagement
Traditional compliance-focused training bores people. Bored people don't learn effectively. Bored people definitely don't change behaviors.
Gamification transforms security training from mandatory obligations into interactive experiences. Organizations implementing gamified elements report 60% increases in engagement and 73% higher completion rates.
Effective gamification incorporates several mechanics:
Achievement badges reward course completion and successful threat reporting, creating positive reinforcement for secure behaviors
Interactive challenges embed learning within engaging formats that improve knowledge retention compared to passive video watching
Leaderboards recognize employees demonstrating exceptional threat awareness, fostering healthy competition for continuous improvement
Security champions programs identify and celebrate individuals who consistently report threats and maintain strong security practices
The results extend beyond engagement metrics. Organizations implementing gamified training report 83% increases in employee motivation and 43% productivity gains. Security awareness integrates seamlessly into daily workflows rather than interrupting them.
The key is balancing game elements with professional content. Your finance team won't respond well to childish graphics or silly scenarios. Effective gamification uses competition, achievement, and progress tracking while maintaining relevance to real threats and business operations.
Measuring Training ROI
CFOs and boards want numbers. They want to know why security awareness training deserves budget when that money could fund other initiatives. Fair question. You need solid answers.
Organizations with robust security awareness programs reduce breach-related costs by an average of $1.5 million compared to those without training. The fundamental equation delivers $4 in value for every $1 invested in security awareness programs.
Direct Cost Avoidance
Breach prevention generates the most substantial ROI. The average data breach costs $4.44 million globally, with phishing-related breaches averaging $4.88 million. Organizations implementing effective training reduce phishing attack success rates by 30-60%. Do the math. Preventing even one breach pays for your entire training program many times over.
Beyond catastrophic breaches, training reduces daily security incidents consuming IT and security team resources. Organizations report $2 million annual savings from decreased incidents requiring investigation and remediation. Each prevented incident means your security team focuses on strategic initiatives rather than responding to preventable user errors.
Faster threat detection by trained employees contains incidents before they escalate. Organizations with weak security awareness spend an average of $1.58 million on containment costs alone. Training that improves detection and response directly reduces these expenses.
Operational Efficiency Gains
ROI extends beyond pure security metrics. Organizations with mature security awareness programs report 62% faster incident response times. Your security teams stop firefighting constant user errors and focus on higher-value projects like threat hunting and architecture improvements.
Help desk efficiency improves measurably. Reduced tickets for password resets, account lockouts, and malware infections free IT resources for strategic work. These operational improvements might not make headlines, but they compound over time into significant productivity gains.
Compliance efficiency provides additional returns. Comprehensive security awareness training satisfies regulatory requirements under NIS2, DORA, GDPR, and PCI DSS simultaneously. You reduce audit preparation time and demonstrate due diligence that may mitigate regulatory penalties if incidents occur.
Organizations achieving security awareness maturity transform training from cost centers into strategic investments with quantifiable business value. The key is establishing baseline metrics before implementing new programs, then tracking incident reductions, response time improvements, and breach cost avoidance. These numbers demonstrate ROI to CFOs and boards in language they understand.
Top 5 Security Awareness Training Platforms
Choosing the right training platform directly impacts your security outcomes. The average data breach costs $4.44 million globally, with phishing-related incidents averaging $4.88 million. Selecting an effective platform potentially prevents these catastrophic losses while delivering $4 in value for every $1 invested.
Platform | Best For | Key Strength | Primary Limitation |
|---|---|---|---|
Brightside AI | OSINT-driven personalization & AI threat coverage | Digital footprint scanning with tri-vector simulations | Newer platform (less market presence) |
KnowBe4 | Large content libraries & established ecosystem | Extensive training modules and integrations | Generic content, limited risk scoring |
Proofpoint | Email security integration | Custom phishing simulations with QR/USB scenarios | No risk scoring, interface issues |
Adaptive Security | Cutting-edge AI threat simulations | Deepfake and generative AI content | Rapid development cycle (frequent changes) |
Hoxhunt | Behavior-first adaptive training | Proven 60% reporting rates | Narrower focus on phishing/social engineering |
Brightside AI
Brightside AI takes a fundamentally different approach than traditional training platforms. Instead of just teaching employees about generic threats, it identifies their actual digital exposure and trains them against real vulnerabilities.
The platform's OSINT-powered personalization scans employee digital footprints across six vulnerability categories: personal information, data leaks, online services, personal interests, social connections, and locations. This scanning reveals work emails exposed on LinkedIn, compromised passwords on the dark web, and publicly available personal data that attackers exploit for spear phishing campaigns.
Training and simulations leverage this real-world exposure. When an employee sees a phishing simulation using their actual exposed data, the lesson hits differently than a generic example. This is their vulnerability. This is how attackers would target them specifically.
Comprehensive attack vector coverage addresses modern threats across three channels. AI-generated email phishing simulations use real OSINT data for maximum realism. Voice phishing simulations deploy AI-powered phone calls training employees to recognize social engineering in voice communications. Deepfake simulations prepare teams for sophisticated video and audio manipulation. This tri-vector approach addresses the 82.6% of phishing emails now containing AI-generated content and the 46% of organizations already targeted by deepfake attacks.
Brighty privacy companion provides interactive guidance through personalized action plans. When the platform detects vulnerabilities, Brighty delivers step-by-step instructions in conversational language, explaining risks and providing specific tips like configuring LinkedIn privacy settings or implementing email aliases. This employee empowerment model reduces corporate vulnerability while respecting personal boundaries.
The dual portal architecture serves both organizational and individual needs. The Admin Portal provides CISOs with organizational security posture visibility, team vulnerability scores, and simulation campaign management without exposing employee personal data. The Employee Portal gives staff direct access to their digital footprint dashboards, guided remediation, and assigned training courses. This privacy-first design builds trust while reducing enterprise risk.
Brightside's Swiss quality standards and award recognition (SecTech Award, Top EU Cybersecurity Startup) position it as an innovative choice for organizations seeking AI-driven security awareness training addressing both employee behavior and underlying digital exposure.
KnowBe4
KnowBe4 maintains the largest market presence with extensive training libraries and established phishing simulation capabilities. Organizations already using KnowBe4 for email security may value ecosystem consistency.
Strengths include deep content libraries spanning basic to advanced cybersecurity concepts, manager escalation features with auto-reminders driving training completion, and LMS integrations. The platform offers gamified modules improving engagement over traditional video-based training.
Limitations center on content quality and adaptability. Users report training content often feels outdated and generic, failing to address current AI-powered threats with necessary sophistication. The platform offers limited risk scoring based on only six human risk factors, providing less granular vulnerability assessment than competitors. Interface performance issues and lack of true adaptive training reduce effectiveness for organizations requiring dynamic, personalized programs.
Proofpoint
Proofpoint focuses on custom phishing simulations integrated with their email security platform. Organizations already deploying Proofpoint for email protection may achieve operational efficiency through single-vendor consolidation.
Strengths include robust phishing simulation capabilities with QR codes, attachments, USB, URL clicks, and credential capture scenarios. The platform provides scheduled automated reminders and gamified modules for improved engagement.
Limitations include absent risk scoring capabilities identifying high-vulnerability employees requiring targeted intervention. Users report sluggish, non-intuitive interfaces frustrating administrators. The platform lacks adaptive training capabilities personalizing content based on individual risk profiles.
Adaptive Security
Adaptive Security specializes in AI-powered training addressing emerging threats like deepfakes and AI-driven phishing through generative AI content creation.
Strengths include cutting-edge deepfake and AI content simulations mirroring real-world threats, OSINT-driven personalization adapting to employee roles and company data, and custom content builders enabling security teams to adjust modules for new threats. Users praise the clean admin portal, fast deployment through two-click integrations, and exceptional customer support.
Limitations center on platform maturity. The solution undergoes rapid development with frequent updates and changes that some organizations may find disruptive.
Hoxhunt
Hoxhunt pioneered adaptive security awareness training delivering 60% phishing simulation reporting rates after one year, compared to 7% for quarterly training approaches. The platform focuses on behavior-first curriculum emphasizing recognition and reporting over passive content consumption.
Strengths include proven adaptive training methodologies with measurable behavior change, multi-channel phishing coverage across email, QR codes, SMS, and voice, and instant feedback mechanisms reinforcing secure behaviors. The platform emphasizes reporting rate and time-to-report metrics rather than completion percentages.
Limitations include narrower focus on phishing and social engineering compared to comprehensive platforms addressing digital footprint management and broader cybersecurity topics.
Regulatory Compliance Requirements
Regulatory frameworks increasingly mandate comprehensive security awareness training, transforming it from optional programs into legal obligations with substantial penalties for non-compliance.
Key Regulatory Frameworks
NIS2 Directive became effective October 17, 2024, expanding security requirements across critical infrastructure and essential services throughout the European Union. Organizations falling under NIS2 jurisdiction must implement security awareness training programs addressing cyber hygiene, risk management, and incident response protocols. Non-compliance exposes organizations to fines reaching €10 million or 2% of global annual turnover.
DORA (Digital Operational Resilience Act) became effective January 17, 2025, mandating financial services entities implement comprehensive ICT risk management including employee security awareness training. The regulation requires evidence of ongoing training effectiveness, driving organizations toward measurable programs rather than annual compliance exercises.
GDPR continues requiring organizations demonstrate appropriate technical and organizational measures protecting personal data, including employee training on data protection principles and breach response. Regulatory authorities increasingly scrutinize security awareness programs during breach investigations, using inadequate training as evidence of negligence when levying fines.
Strategic Compliance Approaches
CISOs should implement training programs exceeding minimum regulatory requirements while maintaining evidence demonstrating due diligence. Documentation should include training completion records, phishing simulation results, incident response metrics, and continuous improvement initiatives.
Multi-framework alignment creates efficiency. Training programs addressing GDPR data protection requirements, NIS2 cyber hygiene mandates, DORA resilience testing, and PCI DSS security awareness obligations simultaneously reduce redundancy while ensuring comprehensive regulatory coverage. You demonstrate compliance efficiency to CFOs by consolidating multiple regulatory requirements into unified training programs rather than maintaining separate initiatives for each framework.
Building Effective Programs
Successful security awareness programs require strategic planning, executive sponsorship, and continuous optimization based on measurable outcomes.
Program Design Foundations
Effective programs begin with baseline risk assessments identifying organizational vulnerabilities, high-risk employee groups, and prevalent threat vectors targeting your specific industry. Analyze historical incident data revealing common attack patterns, then design training addressing these actual threats rather than generic cybersecurity topics.
Role-based training paths recognize that finance teams face different threats than engineering staff or executive assistants. Personalized content resonates more effectively than uniform modules, improving engagement and knowledge retention. Segment employees by risk exposure, tailoring training intensity and frequency to individual vulnerability levels.
Deployment frequency significantly impacts effectiveness. Quarterly training achieves only 7% phishing reporting rates, while continuous micro-learning integrated into daily workflows drives 60% reporting after one year. Implement short, frequent training sessions maintaining engagement without disrupting productivity.
Measurement and Optimization
Comprehensive metrics transform security awareness from compliance exercises into risk management programs with quantifiable business impact.
Track four metric categories:
Behavior metrics including phishing simulation reporting rates and time-to-report suspicious messages
Incident metrics measuring security event frequency and severity
Engagement metrics assessing training completion, time spent, and user satisfaction
Business metrics calculating ROI through breach cost avoidance and operational efficiency gains
Establish baseline measurements before implementing new programs, then track quarterly improvements demonstrating program effectiveness. Metrics revealing persistent vulnerabilities in specific departments or employee groups should trigger targeted interventions rather than universal training increases.
Continuous improvement requires regular program reviews incorporating employee feedback, emerging threat intelligence, and performance data analysis. Update training content quarterly to address new attack techniques, adjust simulation difficulty based on organizational performance, and eliminate ineffective modules consuming time without delivering security improvements.
Executive communication remains critical. Present security awareness metrics to boards and C-suites quarterly, translating technical performance into business language emphasizing risk reduction, cost avoidance, and regulatory compliance. Demonstrating measurable ROI secures ongoing program funding and executive sponsorship essential for cultural transformation.
Start your free risk assessment
Our OSINT engine will reveal what adversaries can discover and leverage for phishing attacks.
FAQs About Security Awareness Training for Employees
What's the goal of security awareness training for employees?
Security awareness training transforms employee behavior from potential vulnerabilities into active defensive capabilities. The primary goal is teaching your team to recognize, report, and respond appropriately to cyber threats.
Organizations implementing effective training achieve 30-60% reductions in successful phishing attacks, with top performers reaching 60% reporting rates on suspicious messages. Beyond attack prevention, training cultivates security-conscious culture where employees understand their role in protecting organizational assets, customer data, and business operations.
Effective programs measure success through behavioral metrics like reporting rates and response times rather than completion percentages. Checking a box doesn't equal changed behavior. Organizations with mature security awareness programs report 47% reductions in identity-related security incidents and 62% faster incident response times. Those numbers demonstrate genuine security improvement, not just compliance documentation.
How often should organizations conduct security awareness training?
Training frequency dramatically impacts effectiveness. Organizations deploying quarterly training programs achieve just 7% phishing simulation reporting rates, while adaptive training with regular micro-lessons drives 60% reporting rates after one year.
Modern best practices recommend short, frequent training sessions integrated into daily workflows rather than lengthy annual compliance events. Organizations should deliver 5-10 minute micro-learning modules monthly or bi-weekly, supplemented by regular phishing simulations testing real-world threat recognition.
This continuous reinforcement maintains cognitive engagement and prevents knowledge decay between training sessions. High-risk employees or those demonstrating vulnerability in simulations should receive additional targeted training addressing specific weaknesses.
Regulatory requirements under NIS2 and DORA mandate ongoing training rather than one-time annual events, pushing organizations toward continuous security awareness models that align with both compliance obligations and genuine security effectiveness.
What happens if employees fail phishing simulations?
Progressive, educational responses to simulation failures generate better outcomes than punitive approaches damaging morale and creating adversarial relationships.
When employees click malicious links or enter credentials in phishing simulations, best practice platforms immediately deliver contextual micro-training explaining what indicators they missed, how the attack attempted to manipulate them, and specific actions for identifying similar threats in the future.
Track repeat failures identifying employees requiring additional support, then provide targeted one-on-one coaching or role-specific training addressing persistent vulnerabilities. Punitive responses like public shaming, manager escalations without context, or disciplinary actions create fear-based cultures where employees avoid reporting suspicious messages to prevent embarrassment.
Effective programs celebrate reporting suspicious messages, even when employees initially interacted with simulations. Recognition and reporting represent successful security behaviors regardless of initial mistakes. Frame simulation failures as learning opportunities revealing training gaps requiring program adjustments rather than individual employee deficiencies.
How does security awareness training improve organizational cybersecurity posture?
Security awareness training improves organizational cybersecurity through multiple interconnected mechanisms reducing both technical vulnerabilities and human risk factors.
Primary improvements include decreased successful phishing attacks, with trained employees recognizing and reporting 30-60% more suspicious messages before clicking malicious links or downloading infected attachments. Organizations with robust training programs reduce breach-related costs by an average of $1.5 million compared to those without security awareness initiatives.
Beyond phishing prevention, training cultivates security-conscious behaviors around password hygiene, multi-factor authentication adoption, safe data handling practices, and appropriate responses to suspicious requests indicating social engineering attempts. Organizations implementing comprehensive programs report 47% reductions in identity-related security incidents as employees recognize credential harvesting attempts, resist MFA fatigue attacks, and maintain stronger authentication practices.
Improved incident response represents another critical benefit. Trained employees report threats 62% faster than those without security awareness education, enabling security teams to contain incidents before they escalate into major breaches. The cultural transformation created by effective training shifts security from exclusively IT responsibilities into shared organizational accountability where every employee actively participates in cyber defense.
What security awareness training topics are most critical for 2025?
Organizations should prioritize training addressing AI-powered threats representing the fastest-growing attack vectors. AI-generated phishing content now appears in 82.6% of phishing emails, with attacks increasing 1,265% since AI tools became widely accessible.
Critical training topics include:
Recognizing AI-generated spear phishing leveraging publicly available employee information for hyper-personalized attacks
Identifying deepfake audio and video impersonating executives or trusted contacts
Understanding vishing attacks using AI-generated voices
Multi-channel phishing awareness covering email, QR codes, SMS, and voice channels
Identity and access management topics including password hygiene, MFA adoption, and credential harvesting recognition remain foundational, particularly as 41% of data breaches begin with phishing as the initial attack vector. Data handling and collaboration hygiene for tools like Microsoft Teams, Slack, and shared drives addresses insider threats and accidental data exposure risks.
Organizations should supplement these universal topics with role-specific modules addressing threats targeting finance teams, executives, human resources, and other high-risk groups differently than general employee populations. Training should emphasize reporting suspicious activities as the primary success metric, cultivating cultures where employees feel comfortable flagging potential threats without fear of punishment for false positives.
How can CISOs demonstrate security awareness training ROI to executives?
Justifying security awareness training budgets requires translating technical security improvements into business language emphasizing financial impact, risk reduction, and strategic value.
Present ROI through three primary frameworks:
Direct cost avoidance: Calculate potential breach costs based on the $4.44 million global average for data breaches and $4.88 million average for phishing-related incidents. Demonstrate how training reduces breach probability through measurable metrics like improved phishing reporting rates and reduced security incidents. Organizations with effective training programs achieve 30-60% reductions in successful attacks, translating directly to avoided breach costs, ransom payments, and business disruption.
Operational efficiency gains: Show 62% faster incident response times freeing security teams for strategic initiatives, reduced help desk tickets from preventable user errors, and decreased security investigations.
Compliance benefits: Demonstrate how comprehensive training satisfies NIS2, DORA, GDPR, and PCI DSS requirements simultaneously, reducing audit preparation time and mitigating regulatory penalty risks.
Establish baseline metrics before implementing programs, then track quarterly improvements in phishing reporting rates, security incident frequency, breach cost avoidance, and compliance documentation efficiency. Present these metrics to boards and C-suites in business terms emphasizing prevented losses rather than technical security statistics. The fundamental equation of $4 in value returned for every $1 invested provides compelling financial justification.
For organizations evaluating new security awareness platforms, consider exploring comprehensive solutions that address both employee training and digital footprint management for maximum risk reduction across your enterprise.
Taking Action on Security Awareness Training
The data tells a clear story. Organizations maintaining traditional quarterly training programs achieve only 7% phishing reporting rates while facing 3.4 billion daily phishing attacks increasingly powered by AI-generated content. Your quarterly compliance exercise isn't protecting your organization.
Next-generation security awareness training delivers measurable results through adaptive, continuous learning models that reduce successful attacks by 30-60% while achieving $4 in value for every $1 invested. Organizations implementing AI-powered simulations, OSINT-driven personalization, and employee empowerment models report 47% fewer identity-related incidents and 62% faster threat response times.
Evaluate your current program against 2025 best practices by asking three questions:
Does your training adapt to individual employee risk profiles, or does everyone receive identical content? Do your simulations mirror the AI-powered deepfakes, vishing attacks, and hyper-personalized spear phishing employees face daily? Are you measuring behavioral outcomes like reporting rates and response times, or merely tracking completion percentages?
Organizations ready to transform their security awareness programs should begin with comprehensive platform evaluations, baseline risk assessments establishing current performance metrics, and executive alignment securing funding and sponsorship required for successful implementation.
The security landscape of 2025 demands training programs as sophisticated as the threats employees face. Organizations maintaining outdated approaches accept unnecessary risk while competitors implementing next-generation solutions reduce breaches, save millions in potential losses, and cultivate security-conscious cultures that actively defend organizationalllions in potential losses, and cultivate security-conscious cultures that actively defend organizational assets.